Ever wondered how your favorite video games and sci-fi movies are made? What gives them that realistic look and feel?
3D modeling is the craft of using specialized computer software to create three-dimensional representations of an object or a surface. From video games to architecture, 3D modeling is an extremely important addition to our lives, helping creators make photo-realistic models.
On a broad level, 3D modeling involves the manipulation of edges, vertices, and polygons in a simulated 3D space. You can determine an object’s size, shape, and even texture.
3D models help build a physical body from a collection of points in space, all connected by geometric entities such as triangles, lines, curved surfaces, etc.
How does 3D modeling work?
Before we break down the 3D modeling process into its individual elements, let us understand it in a general sense. A 3D model is essentially a” with “collection of vertices from edges and collection of edges from polygons which give us a complete mesh. This mesh is the core of any model. In other words, every individual change you make is on this mesh, as you build it up. Utilizing coordinate data, the modeling software recognizes the location of each vertical and horizontal point, relative to a reference point.

When a 3D modeling project starts, the general way to begin is by picking up a basic shape – it could be a cube, cone, sphere, etc. Having a basic shape helps you build your model over it. It also reduces efforts by allowing you to manipulate its vertices instead of having to work without a reference. From this starter shape, you can begin refining and altering its dimensions to achieve the shape you desire.
What is 3D modeling used for?
So where are 3D models actually used? You would be surprised to know that numerous industries utilize 3D modeling for a range of projects; there are likely loads of 3D modeled items we use without even realizing its involvement. With 3D modeling, the opportunities are endless. It’s a truly versatile medium that can be used for an array of different areas. Let’s explore some common uses of 3D modeling:
Game development
The need for 3D modeling was first felt by game developers. As games aimed to become more realistic, its characters and surroundings had to be upgraded to match modern standards.
3D models are now used to create photo-real characters, props, and immersive worlds, within video games. The result is enchanting visuals and an overall unique experience.

But the real importance of 3D modeling lies in the world of VR gaming. VR stands for Virtual reality, where through a device, you can experience a whole new reality that has been created virtually for you. It is not real, but constructs visuals that resemble a parallel reality. VR can literally place you within the action, as you feel the experience from a 1st person Point of View.
3D printing
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is the creation of three-dimensional solid objects using a digital 3D model file.
In simple terms, it involves the deposition of appropriate material over powdered grains, plastics, or even liquids, to fuse them into a homogenous layer. These layers are then made to solidify in a controlled environment, to create models that mimic real-life figures.

To visualize the process, consider these layers to be thinly sliced cross-sections of the desired shape, which is stacked slowly to create the final project.
Since the process involves the use of ‘additive processes’, where successive layers are joined to give volume and dimensions to a model, it is called additive manufacturing.
3D modeling is the process that makes 3D printing possible. Without the creation of models, you would have no input for the 3D printer. The 3D printer follows the digital model and prints physical copies, breathing life into your creations.
Not only that, 3D models play a vital role in driving sales. Adding 360 degree views of your product on your website creates an interactive experience for your clients, and gives an overall uplift to your brand image.
And sustainable product design is a great step in the right direction.
Architecture

Architecture relies heavily on planning. Without a solid roadmap, you would be wasting time, effort and finances. Here’s where 3D models make the job easier. 3D modeling allows architects to go beyond conventional hand-drawn building plans. At every step of a construction, they can make changes and modifications to the 3D model, which makes both planning and implementation more streamlined. 3D modeling can also reveal potential issues with structures before they are constructed, a feat impossible to achieve by 2D plans.
Animation
The animation industry heavily depends on 3D models to create visually appealing and wacky imagery. From cartoons, to anime, without 3D models, we would never have access to the kind of content we have grown to love. A 3D model, once prepared, can be completely rigged and animated.
Today, most animated movies utilize some form of 3D programming. Perhaps that is the reason why the quality of your favorite 3D movies seems to have elevated.
Product design
The design industry also uses 3D modeling to visualize their prototypes before they begin manufacturing. This not only recognises any design errors, but also reduces material wastage at later stages. It is also less wasteful than repeatedly making mock-products, which serve no purpose after being discarded.
Product Configurators
3D configurators are powerful tools that allow customers to personalize and customize products to their specific needs and preferences in real time.
This not only increases customer satisfaction but also reduces the number of returns and exchanges.
These tools can be used in a variety of industries, including furniture, automotive, and fashion.

A huge advantage of 3D configurators is that they streamline the manufacturing process. Instead of producing products in bulk, manufacturers can produce products on-demand based on customer orders. This reduces the amount of excess inventory and waste, leading to a more sustainable manufacturing process.
Additionally, 3D configurators can also help companies gather valuable customer data. By tracking which design options are the most popular, companies can optimize their product offerings and better understand their customers' preferences.
3D Models can be created in several ways, some of which include:
1. Polygonal modeling –
The most widely used form of 3D modeling, this process is preferred for its quickness and versatility. More concept-driven rather than measurement driven, it is the preferred method of choice when priority is on artistic vision rather than strict dimensions.
Vertices, which are essentially points in 3D space, are arranged in the desired pattern and then connected by line segments to form a polygon mesh (kind of like a constellation of stars). Textured polygonal models, which are used everywhere these days, are flexible blueprints which can be rendered very quickly by computers.
But let's dive into its details.
The core workspace of a mesh model is a vertex, which is a singular point in three-dimensional space. It's from this vertex that the journey of a 3D model starts. To begin creating a 3D model from scratch, two vertices are connected by a straight line to form an edge. Three edges join to form a triangle, which is actually the simplest polygon in Euclidean space. As you keep connecting such triangles, more complex polygons can be created. But most of the time we skip this polygon and work with 4 sided faces called quads.

As you begin building a shape by connecting a group of polygons with shared vertices, you obtain what is called an element. And finally, each of the polygons forming an element is called a face.
Since 3D modeling is almost always carried out using specialized 3D software, a wide variety of 3D graphics packages can be used to construct polygon meshes.
One of the more commonly used methods of constructing meshes is box modeling, which uses two simple tools:
- The subdivide tool, which breaks faces and edges into smaller pieces by increasing the number of vertices. For instance, 4 smaller squares can be made by splitting a larger square.
- The extrude tool is applied collectively to a face. ‘Extrude’ literally means thrust or force out. Using this command, a new face of the same size and shape can be created, and added to each of the existing edges by a face
But all said and done, you cannot settle for straight lined models and may often have to create curved surfaces. In such a case, polygon modeling proves to be cumbersome as you need many polygons to create curves.
2. Curve modeling
In this method, surfaces are not merely restricted to straight lines and are defined by curves. These curves have weighted control points, which it follows to achieve its bends.
If you've used any of the 3D programs like Blender or Maya, a word that keeps popping up is: NURBS curves. Has this left you confused too?
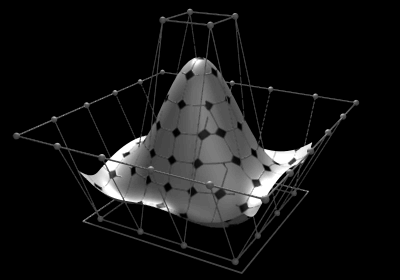
NURBS stands for non-uniform rational Basis spline. NURBS in 3D modeling are what are used to create curved surfaces. The magic of Math now allows you to upgrade from ONLY straight lines to now add gentle slopes and graduations. Basically, B-splines plot out the curves using a collection of control points instead of resorting to a group of polygons. SO essentially, you obtain slopes with the fewest possible "knots" or "elbows".
As mentioned before, pure polygonal geometry makes it painstakingly hard to construct curves, but NURBS curves make this design possible.
3. Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is another unique and fun way of generating 3D models. Instead of sitting behind a computer, this process starts somewhere else. Here, you use a camera to click photographs of an object from all angles.
And then the process of representation starts. Once you are satisfied with the angles and lighting, you feed these images into a program that reads, interprets and generates a 3D representation of the object.

One of the main advantages of this method is that you get real-world inputs for your model, hence whatever you create will be the closest to realism. Plus, since we photograph whole, completed objects, textures and UV Maps often get pre-generated in the process.
But the biggest downside of photogrammetry is that however hard you try and no matter the quality of your camera, the photograph will need extensive cleanup. Sometimes the surroundings are captured while other times your photographs may have missed a small chunk of the object, rendering your model incomplete.
4. Boolean modeling
Boolean algebra is a part of algebra where the variables are the truth values: true and false, denoted by 1 and 0 respectively. When we add the same logic to 3D modeling, boolean modeling is obtained where we start with a whole model and omit or add objects to create a new shape.

Usually, basic shapes are individually modeled with box modeling and subsequently combined with boolean operations. These operations include:
- Difference
- Union
- Intersect
Among these, the difference operator is most commonly used where the operator cuts away the shape to reduce the volume of an object.
With Union, two objects are merged together to form one.
Intersect saves only the geometry shared by two or more objects and deletes the rest.
4. Sculpting
Sculpting in 3D modeling is an art form that allows artists and designers to create intricate and detailed models using digital tools. The process of 3D sculpting is similar to traditional sculpting, but with the added advantage of being able to manipulate the digital model in ways that would be impossible in the physical world.
One of the main benefits of 3D sculpting is its versatility. Artists and designers can create models of virtually any shape or size, from small figurines to large architectural structures. The process is also incredibly precise, allowing for fine details to be included in the final product.

Another advantage of 3D sculpting is its speed and efficiency. Unlike traditional sculpting, which can take weeks or even months to complete, 3D sculpting can be done in a matter of hours or days. This allows artists and designers to quickly iterate on their designs and make changes as needed.
Additionally, 3D sculpting is highly collaborative. Multiple designers can work on the same model simultaneously, making it easier to create complex designs that require input from multiple people.
Types of 3D modeling software
Your 3D model is only as good as the software it is created on. With so much variety within 3D modeling, it is only natural to have several different software, each with its own set of functionalities at your disposal.
These software come in different price ranges, serve different purposes and have some differentiating factors. Here are some examples of 3D modeling software:
1. Blender
Widely popular among 3D modeling artists, both for its ease of use and multiple functionalities, this is an open-source software that is available to download for free. It’s a great place to start your 3D modeling journey, since there are several tutorials on YouTube and Udemy to guide you through the operations of Blender.
Blender supports numerous CAD features like modeling, rigging, rendering, composting and motion tracking. Plus, it is compatible with a 3D printer!
2. Autodesk Maya
Maya is perhaps the most powerful 3D modeling software at present. and is mostly used for animation (even by leading animation studios). It is also a lot more advanced than Blender, when it comes to realistic animations. Plus, it is incredible at motion-capture handling .
Maya also allows you to apply modeling layers instead of using modifiers. Maya is also the gold standard when it comes to nurbs modeling.
Perhaps one of the greatest downsides of Maya is that it is a lot more expensive than other available softwares. Plus, if you are a beginner, it would probably be a better idea to start with Blender, as Maya is a lot more difficult to master, considering its many additional features.





